‧
9 min read
Become a data analyst in 2026: a practical roadmap
Abed Habli and Robert Kosara
‧ 9 min read
Share this article
Becoming a data analyst is both a great goal and a big undertaking. It’s tempting to try to list everything you might need to learn, but that quickly becomes overwhelming and still incomplete.
Instead, this guide gives you a solid starting point. It focuses on building a strong foundation that will support all the topics you’ll want, or need, to learn later. The topics are broken down below into chunks of related topics, and organized by tools you might know or want to learn: Spreadsheets, Metabase, and SQL.
Stay tuned for part 2, which will include pointers to more advanced topics for you to tackle once you’ve mastered the basics laid out here.
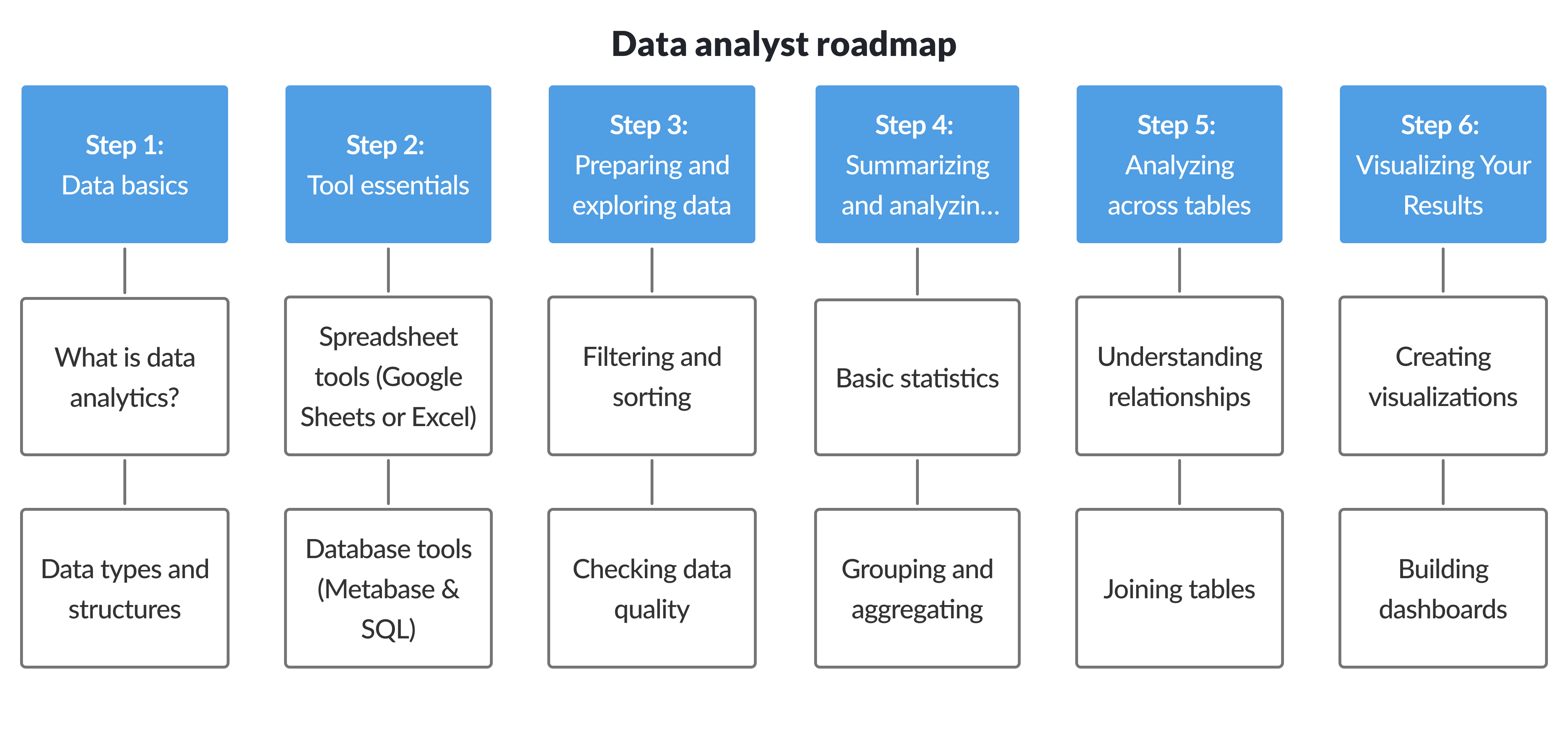
Step 1: Data basics
First, let’s look at what data and data analytics even are. This is the foundation for all further steps. Even if you’re familiar with some of the material here, it will pay off to remind yourself of these fundamental concepts.
Data analytics fundamentals
Analytics is all about understanding what your data means and what it can tell you about your business (or whatever your data is about). Analytics serves a number of purposes, and doesn’t just react to the data. There are different types of analytics you should be aware of, even if we are mostly covering descriptive analytics in this guide.
Core concepts
- What data analysts do, explained in this expert guide
- The main types of analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive
- The difference between data science and data analytics
Data types and structures
Data comes in many forms, but we’re really only looking at a fairly specific kind of data here: tabular data the way it is used in spreadsheets and databases. Much of the worlds of business and technology run on this kind of data, however. In this section, we’re looking at how this data is organized and what kinds of information you can find in databases and spreadsheets.
- How data tables work, including rows and columns
- The difference between quantitative and qualitative data
- Understanding discrete vs continuous variables
- What structured and unstructured data mean
- Why data granularity matters
- Additional reading on numerical and categorical data
Step 2: Getting started with your tools
Before diving into analysis, you need to get comfortable with your tools. The three most common are Excel (for spreadsheets), Metabase (a BI tool), and SQL (for querying databases).
Start with whichever tool is most relevant to your work. You don’t need to learn all three at once.
Excel basics
You can skip this if you’re comfortable in Excel, but take this opportunity to reacquaint yourself with the basics of spreadsheets if you’re unsure.
- An overview of essential formulas like
SUM,AVERAGE,COUNT,IF, andVLOOKUPin this Excel tutorial
Metabase basics
As a BI tool, Metabase allows you to work directly with databases without necessarily knowing SQL, and also create data visualizations.
- An introduction to core Metabase concepts in the Metabase basics overview
SQL basics
SQL is the native language of databases. Even if it might look difficult, it’s worth knowing for more complex data analysis (and because it’s the industry standard). It’s also much less scary than it initially looks, once you get to know it a little bit.
- A beginner-friendly SQL introduction from Metabase
- Hands-on practice with SQLBolt’s interactive lessons
- A concise SQL cheat sheet for quick reference
Step 3: Exploring and preparing data
Now let’s get to the actual work with data! The first step is being able to organize it. Filtering and sorting data are the first operations, and they are part of all the next steps below.
The good news is that once you understand the concept in one tool, it transfers easily to others.
Filtering data
-
Filtering in Excel Learn how to narrow down rows in spreadsheets using built-in filters, as shown in this Excel filtering guide.
-
Filtering in Metabase Apply filters visually in the query builder without writing SQL, as explained in the Metabase filtering guide.
-
Filtering in SQL Filter rows in database queries using
WHEREclauses, text and date conditions, and logical operators likeAND,OR, andNOT, using examples from filtering by text and filtering by date.
Data quality
Data is rarely clean and perfect. It may come from multiple sources, use inconsistent formats, or contain missing values.
- Learn how to prevent errors using data validation in Excel
- Understand different strategies for handling missing values in this guide to data cleaning
- Format and clean results directly in Metabase using question formatting options
- A checklist covering common data cleaning tasks in this data cleaning checklist
Step 4: Summarizing and analyzing data
Once your data has been checked and cleaned, and you’re able to perform basic sorting and filtering, the more advanced operations can begin. Data can be vast, so it is necessary to reduce it in different ways to make sense of it. This is done using various kinds of aggregations: groupings that compute values. They can be simple sums, or various statistical values like means or medians.
Basic statistics
You’ve heard of means and medians, but what do they mean? And how are they computed?
- An explanation of mean, median, and mode in this statistics overview
- An introduction to statistics concepts commonly used in data analysis in Basic statistics for data analysis
It’s also useful to understand data aggregation, how individual data points are grouped into summary values. See this data aggregation overview.
Aggregation in Excel: Pivot tables
Pivot tables are a powerful way of computing aggregations in spreadsheets. While they might seem daunting at first, the basic idea is the same as in SQL: subdivide the data and compute values over each segment. Much of data analysis is built on top of this approach.
- Learn how to create them with Microsoft’s pivot table guide
- Read why they matter in this Reddit discussion on pivot tables
- See a visual explanation on Wikipedia’s pivot table page
Aggregation in Metabase
Similarly to Excel, Metabase has the tools for computing sums and breaking down large datasets into sections.
- Learn how to summarize data using the Metabase summarize feature
Aggregation in SQL: GROUP BY
The SQL way of computing aggregations and statistics is done using the GROUP BY keyword. These resources will help you understand how it works.
- A clear explanation of
GROUP BYin this SQL guide
Metrics and KPIs
Once you can aggregate data, the next step is deciding what to measure. Metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) help turn raw numbers into signals you can track over time and use to guide decisions.
- An overview of common business metrics in Essential SaaS metrics
- Tips for designing better metrics in How to design better metrics
Step 5: Analysis across data tables
In real databases, data is usually organized into several data tables. To answer questions, these have to be connected through joins. This section explains how joins work, and how this operation can be performed even in Excel, but also in a BI tool like Metabase and using SQL.
XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP in Excel
To combine data from different tables, Excel has the XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP functions.
- See how spreadsheet lookups relate to database joins in From XLOOKUP to joins
Joining tables in Metabase
In databases, this operation is called a join. Metabase can create joins in its query editor.
- Learn how joins work in the Metabase joins guide
Database joins in SQL
SQL of course allows you to create joins using the JOIN keyword.
- A practical introduction to joins in SQL joins explained
Step 6: Data visualization and dashboards
Finally, once your analysis is done, it is time to show your results to the world. The way to do this is using charts and visualizations. Here we cover the basics of creating visualizations from data, and how to turn them into a interesting and compelling story.
Visualization fundamentals
- Learn how to visualize trends with time series charts
- Improve chart clarity with better line and bar charts
- Explore geographic data using maps and geospatial visualizations
- Choose the right chart with this visualization guide
Designing clear dashboards
- Understand what dashboards are in this Coursera overview
- Avoid common mistakes highlighted in Top dashboard fails
Data storytelling
- Learn what data storytelling means in this introduction
- Improve clarity by reducing clutter, as explained in What clutter can we eliminate?
- Build better charts with the idea of a clear graph skeleton
Conclusion
Data analysis is a fascinating field to dive into, but it is easy to get lost in the many different things you can do, and all the possible ways to do it. If you’re new to this field, our guide will give you a first foundation for you to then base your own explorations on.
We very consciously kept this guide quite simple and basic. It’s better to have a shorter list of items to really work through, than a massive list that you have no hope of ever completing.
In a few months, we will follow up with more advanced tutorials and topics, so stay tuned!